
Support greater loads over longer distances. Rafters provide low levels of support to the roof structure.
#Rafter vs truss plus
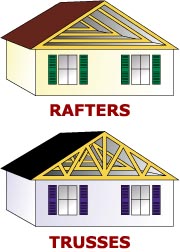
Strapping is used to brace, space, and level trusses to form the roof.Ī rafter roof requires two opposing birdsmouth notched and plumb cut rafters with a collar tie and a ceiling joist spaced accordingly along a ridge board or beam, plus purlins, props, cleats, and struts spaced as required. Manufactured using 2x3, 2x4, and 2圆 dimensional lumber fastened with metal gussets.Ģ圆 to 2x12 lumber or larger 4”, 6”, 8”, or wider timbers of greater depths.Įach truss is comprised of one or two sloping top and bottom chords, plus internal geometric bracing of diagonals and or verticals. Greater design freedom for more complex roof lines The span also determines additional support requirements. The slope and span determine the rafter thickness and depth. However, there are numerous differences between the two as shown in the table below.ĭesigned and engineered to span greater distances using triangular-shaped webbing. Trusses and rafters are similar in that they form the slope and support the roof deck of a roof structure. Rafters also provide support to gable end walls, and may be partially carried by a ridge beam supported at each gable end, and also elsewhere along the beam. to share and spread the load down and outward to the support walls. Rafters are measured and cut individually and installed one at a time, so they are more labor-intensive.Ī rafter can’t stand alone and requires other components, like a ridge board or beam, oppositional rafters, purlins, purlin props and cleats, struts, collar ties, ceiling joists, etc. A rafter is the angled component of a roof’s structural framework that sets the slope of the roof deck and is manufactured onsite and in place. Rafters are the traditional stick framing method used for roofing buildings, they run from the ridge or hip to the supporting exterior wall.

The end roof trusses typically are designed to be both a truss and to form the gable end wall. Trusses are usually fastened to each other at specified points and rest upon the wall structure so the load is transferred vertically or in a downward, not outward direction.
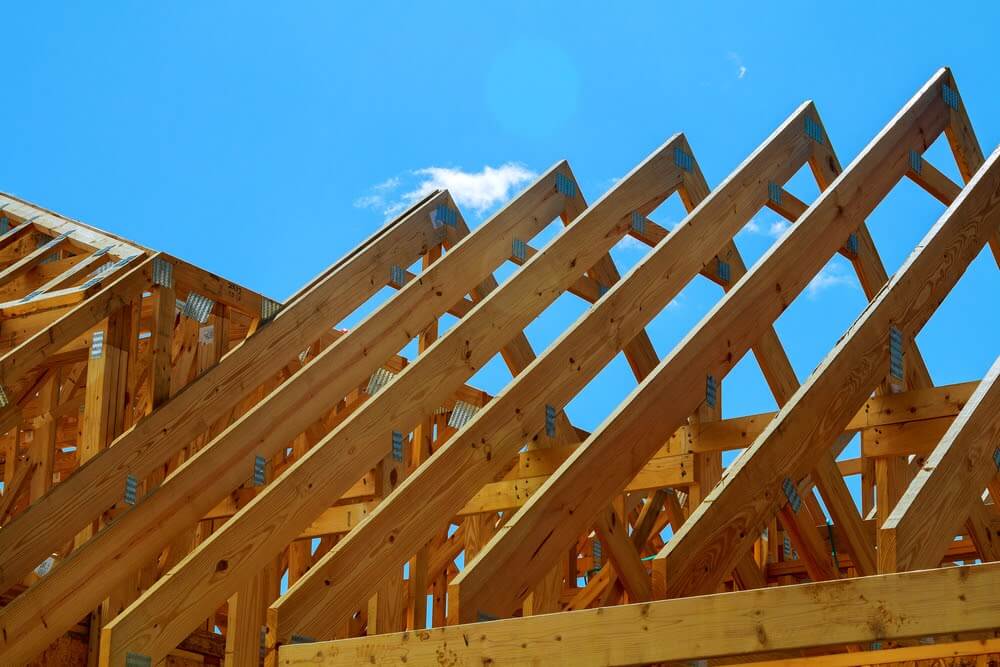

Roof trusses are constructed to span specified distances at a set spacing to sustain calculated loads. Roof trusses typically are stand-alone frameworks composed of horizontal, diagonal, and vertical struts that form triangular shapes made of wood with steel plates fastening components together. They are pre-ordered, manufactured offsite, and delivered to the building site. Roof trusses are engineered roof frameworks that provide aesthetic and structural shape to a roof. What Is the Difference Between Trusses and Rafters?.Hopefully, you’ll develop a better understanding of roof frameworks available, and which is best suited for your project. We’ll discuss the pros and cons of trusses and rafters, compare trusses to joists and beams, and rafters to joists, and then identify which is better, rafters or trusses. In this article, we’ll explain what roof trusses and rafters are, identify their similarities and differences, and explore different types of trusses. Rafters are one component of a stick-framed roof structure and are individually measured, cut, and installed, and require other components for support.
#Rafter vs truss install
Trusses are engineered and manufactured off-site to exacting standards and are quick and easy to install as they are freestanding. They form the roof structure and slope of the roof deck. Rafters and trusses serve similar purposes. When selecting the roof framework, though, which is better, trusses or rafters. You get to determine the floor plan, building materials, finishes, and roof structure. Building a house, cabin, shed or garage is a rewarding experience.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
